The Eleven Most
Implanted Medical Devices In America
Implanted medical devices are one
of the most profitable businesses of the U.S. healthcare industry.
24/7 Wall St. has examined
National Health Survey data, multiple professional physician services,
peer-reviewed journals, and SEC filings to complete a list of the most
frequently implanted medical devices today. While many of these are life saving,
controversy swirls around several others.
Many of the devices implanted are
medically necessary and do their jobs extending lives and improving quality of
life, the 24/7 Wall St. research shows. Some products, such as artificial knees
may even be under-utilized. Others, like implantable cardio defibrillators, may
be over-utilized. What is certain in most of the cases reviewed is that the
effectiveness of these devices is not as well researched or understood as their
widespread use may imply.
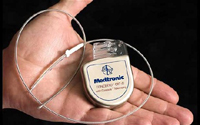 11. Implantable Cardioverter
Defibrillators 11. Implantable Cardioverter
Defibrillators
Cardiac arrhythmia, or improper
electric signaling in the heart, occurs in millions of people a year. While the
vast majority are benign, a select few usually in patients with a history of
heart attack or heart failure can be fatal if not treated promptly. Implantable
cardioverter defibrillators (ICDs) are devices that monitor and treat these
rhythms when they are detected by sending a large jolt of electricity to the
heart, and basically pressing the reset button. Newer models can also function
as pacemakers, combining two devices into one. Complications of ICDs are similar
to their pacemaker siblings: 1%-2% rates of infection and up to a 4% rate of
lead failure. While these devices are major life-saving technology, the U.S.
Department of Justice has been investigating the industry due to the widespread
practice of implanting the devices too soon after a major cardiac event.
 10. Artificial Hips 10. Artificial Hips
As people age and gain weight the
wear and tear on their joints builds up. In particular, more than 20 million
Americans suffer from degenerative osteoarthritis, which is the leading cause of
chronic disability in the U.S. As one of three major weight bearing joints in
the leg (the others being knees and ankles), hips are put under a lot of stress
over a lifetime. This stress commonly leads to the wearing down of cartilage and
the painful friction of bone rubbing against bone. Hip replacement can lead to a
decrease in pain and an increase in mobility in over 90% of recipients. But when
friction or a faulty manufacturing process wears down the replaced joint at a
faster rate than anticipated, replacement of the hip can be necessary earlier
than expected. These failures, in addition to requiring a new hip replacement,
can leave behind fragments that can become focal points for infections, cause
nerve and vessel damage, and possibly even lead to death.
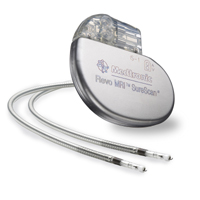 9. Heart Pacemakers 9. Heart Pacemakers
As with ICDs, pacemakers are used
to treat abnormal rhythms in the heart. While ICDs treat otherwise fatal
rhythms, pacemakers are used when the heartís internal clock is not maintaining
a fast enough pace. Pacemakers override the aberrant signals in the heart by
passing small jolts of electricity to multiple parts of the heart muscle,
providing its own rhythm. Modern pacemakers will increase with exercise and
decrease with rest to meet the bodyís minute to minute needs. Complications of
the surgery include a 1%-2% rate of either shortor long-term infection and, more
importantly, up to a 4% rate of lead malfunction.
 8. Breast Implants 8. Breast Implants
Breast augmentation with implants
is the most frequently performed plastic surgery procedure in the U.S., beating
out nose jobs, eyelid surgery, and liposuction by a significant margin. Due to
the increased public criticism, the FDA has since closely monitored breast
implants in the U.S.
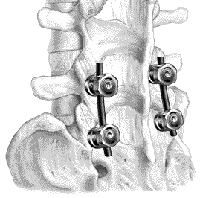 7. Spine Screws, Rods, and
Artificial Discs (Spinal Fusion Hardware) 7. Spine Screws, Rods, and
Artificial Discs (Spinal Fusion Hardware)
Spinal fusion surgeries are
performed for a variety of back problems, mainly for pain and weakness. The
surgery essentially fuses two or more vertebrae with the help of hardware such
as screws and rods. An alternative in a number of these cases and a simpler
procedure overall, decompressive surgery removes part of the bone to free a
trapped nerve. Patients of these fusion surgeries are most likely to have the
least amount of benefit.
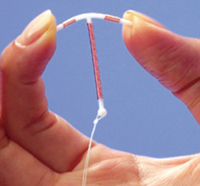 6. IUDs (Intra-Uterine
Devices) 6. IUDs (Intra-Uterine
Devices)
IUDs are extremely popular
worldwide and are the preferred method of contraception for almost 25% of women
in the rest of the developed world. The most serious complications associated
with the devices today are uterine perforation, which occurs in 0.1% of
patients, and pelvic inflammatory disease (PID), which occurs in 0.2% to 0.9% of
patients. Two forms of IUDs are available in the U.S., with an approximately
even split of market share: Paragard, a generic copper-coated IUD offered by
Teva Pharmaceutical Industries Ltd; and Mirena, a progesterone-releasing IUD
offered by Bayer HealthCare.
|

